By quanyu lee
2025-08-18 08:22:33
The difference between wire harnesses and cable assemblies
Wire harnesses and cable assemblies are both essential components for power and signal transmission, but they differ significantly in design, structure, function, and application. Understanding these differences helps engineers and purchasers select the right solution for their specific needs.
The basic difference between wires and cables
Wire: A single strand of electrical conductor, such as copper, aluminum, or steel.
Cable: Two or more insulated wires bundled together and encased in an outer sheath for added durability and organization.
Despite having Wire Harness in the name, a wire harness can actually contain cables as well.
Functional positioning and core differences
Wire Harness:
A systematic assembly that bundles and secures multiple wires or cables according to specific rules. It typically includes connectors, terminals, and other components. Its primary function is to organize wiring and connect internal equipment.
Cable Assembly:
A system consisting of one or more cables, connectors, and plug-ins. It emphasizes protection and stable power/signal transmission and is often used in harsh environments.

Structure comparison table
Characteristic |
Wire Harness |
Cable Assembly |
| Transmission signal type | Low frequency signal, control signal, small and medium power | High frequency signal, high power |
| Core functions | Systematic connections within the device | Stable power/signal transmission |
| Typical applications | Internal circuits of automobiles, home appliances, and electronic equipment | Communication base stations, radar systems, power transmission, aerospace equipment |
| Environmental requirements | Indoor use, low requirements on environmental adaptability | Adapt to harsh environments (high temperature, high pressure, humidity, corrosion, etc.) |
Protect vs. Organize
Wire Harness:
A bundle of multiple wires or cables, typically covered in a jacket, but with the ability to separate individual wires. Its primary purpose is organization and ease of installation, but it offers limited protection.
Cable Assembly:
A bundle of multiple wires tightly enclosed in a single protective jacket creates the appearance of a thicker cable. Its advantages include resistance to moisture, heat, abrasion, compression, and corrosion, making it well-suited for harsh outdoor environments.
Manufacturing process
Wire Harness:
Steps: Wire cutting, stripping, terminal crimping, connector assembly, and bundling.
Process Requirements: Focus on wire arrangement and secure bundling to ensure reliability and stability.
Cable Assembly:
Steps: Wire cutting, stripping, and precision welding, crimping, or other connection methods between the cable and connector.
Process Requirements: Due to the high-frequency signal or high-power transmission involved, the process demands are higher. Ensure that the cable shield and insulation are intact, and that the connections are secure.

Application areas
Cable Assemblies:
Commonly used in military, aerospace, construction, agriculture, communication base stations, and medical devices requiring high-speed data transmission.
Wire Harnesses:
Commonly found in everyday appliances and electronic products (computers, televisions, monitors, microwave ovens, refrigerators), as well as the internal circuits of automobiles and aircraft.
How to choose?
Indoor/Normal Environments → Choose a Wire Harness (lower cost, better organization, and adequate basic protection).
Outdoor/Harsh Environments → Choose a Cable Assembly (highly protective and resistant to extreme conditions).
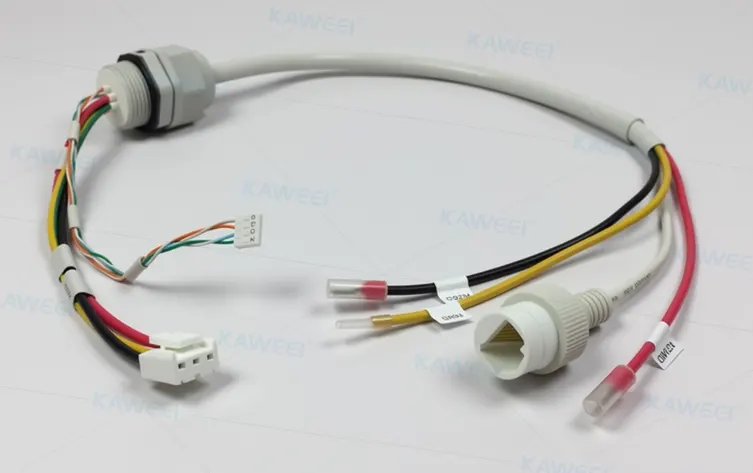

FAQ
Q1: What is the biggest difference between wire harnesses and cable assemblies?
A1: Wire harnesses are primarily used for organization and internal connections within devices, making them suitable for indoor environments and those with less stringent environmental requirements. Cable assemblies, on the other hand, prioritize protection and stable transmission, making them suitable for outdoor use and harsh environments.
Q2: What applications are wire harnesses suitable for?
A2: Wire harnesses are commonly found in automobiles, home appliances, computers, televisions, refrigerators, and the internal circuits of electronic devices.
Q3: In which industries are cable assemblies commonly used?
A3: Cable assemblies are commonly used in military, aerospace, communication base stations, medical equipment, and power systems, particularly in applications requiring high-frequency signal or high-power transmission.
Q4: What are the differences in manufacturing processes between wire harnesses and cable assemblies?
A4: Wire harness manufacturing focuses on wire cutting, stripping, crimping, and bundling, with an emphasis on wiring organization. Cable assemblies require precision welding and crimping, and place higher demands on shielding and insulation protection.
Q5: If I need a custom wire harness, how should I choose one?
A5: Professional manufacturers like Kaweei can provide customized wire harness solutions based on customer needs, including multi-wire bundling, connectors, and terminal configurations, ensuring efficient and reliable power and signal transmission.



