By quanyu lee
2024-12-31 06:50:22
Welding Guide: In-depth understanding of principles, applications, and selection techniques
In modern manufacturing, ultrasonic welding is a highly efficient, environmentally friendly, and precise welding method widely used for joining plastic products, electronic components, and automotive parts. Compared to traditional welding methods, it requires no additional materials, is faster, and is more environmentally friendly. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of the principles, equipment types, application scenarios, and purchasing recommendations for ultrasonic welding, helping engineers and production managers make more informed decisions.
1. What is Ultrasonic Welding?
Ultrasonic welding is a welding technique that uses high-frequency mechanical vibration to directly transfer heat to the material contact surface, achieving intermolecular fusion. In simple terms, it generates frictional heat through high-speed vibration, causing plastics or metals to melt and bond together at the contact surface rapidly.
Unlike traditional welding, ultrasonic welding:
- requires no welding materials (such as welding wire or solder paste)
- is fast, typically completed in seconds
- offers high precision, suitable for small or precision parts
- is environmentally friendly, avoiding harmful gases and high-temperature heat effects.
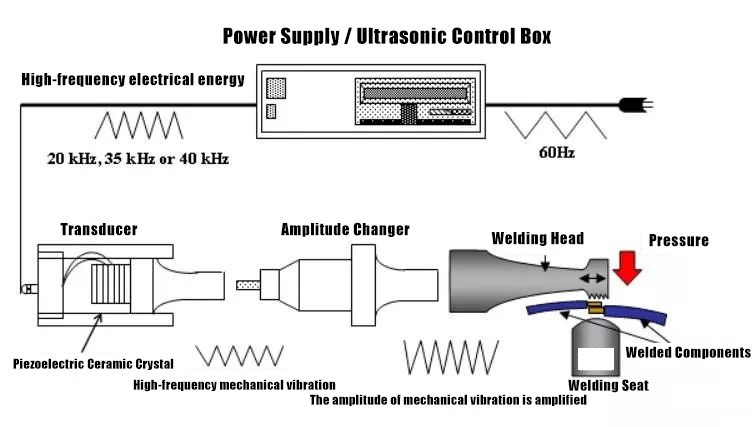
2. Working Principle of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding mainly consists of four parts:
- Ultrasonic generator: Converts electrical energy into high-frequency mechanical vibration.
- Transducer: Amplifies the vibration signal and transmits it to the welding head.
- Welding head (Horn): In direct contact with the material, transmitting vibration to the welding surface.
- Workpiece clamp: Keeps the part stable during the welding process.
Working process:
High-frequency vibration is transmitted to the workpiece contact surface through the welding head, generating frictional heat that melts the material. Subsequently, the vibration stops and pressure is applied, allowing the contact surface to cool and form a strong bond.
3. Application Areas of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding applies to a variety of industries, mainly including:
Automotive Industry
- Dashboard Components, Door Panel Interiors, Sensor Housing Welding
- Improved welding speed and precision, suitable for mass production
Electronics & Electrical Appliances
- PCB Housings, Mobile Phone Parts, Connector Packaging
- Fine welding, no damage to sensitive electronic components
Medical Devices
- Syringes, Reagent Kits, Disposable Medical Supplies
- Ensuring airtightness and hygiene requirements
Packaging Industry
- Food and Cosmetic Packaging Bag Sealing
- High-speed sealing without contamination
4. Types of Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
Based on application requirements, ultrasonic welding equipment can be divided into:
1. Manual Ultrasonic Welding Machine
- Suitable for small-batch production and laboratory use
- Flexible, but relatively inefficient
2. Semi-automatic Ultrasonic Welding Machine
- Human-machine collaborative operation, improving production efficiency
- Commonly used in small and medium-sized production lines
3. Fully Automatic Ultrasonic Welding Machine
- Integrates robotic arm and conveyor system
- High-speed, high-volume production, suitable for industrial applications
5. Key Considerations for Selecting Ultrasonic Welding Equipment
When selecting equipment, the following key factors need to be considered:
1. Welding Frequency
- High frequency (approx. 40kHz) is suitable for welding thick parts and large areas.
- Low frequency (approx. 20kHz) is suitable for precision small parts and thin-walled parts.
2. Welding Head Design
- Customized welding heads based on part shape to ensure uniform welding.
- Welding head material must be wear-resistant to extend service life.
3. Power and Pressure
- Power affects the melting speed and weld depth.
- Pressure ensures weld strength and bond quality.
4. Automation Level
- Manual or semi-automatic options are available for small batches.
- Fully automatic equipment is recommended for large-scale production.
5. Supplier and After-Sales Service
- Prioritize manufacturers with extensive experience who offer customized welding heads and technical support.
- Ensure convenient equipment debugging and maintenance.
6. Advantages and Challenges of Ultrasonic Welding
Advantages:
- High speed and production efficiency
- High precision, suitable for complex and precision parts
- Environmentally friendly, no welding materials or harmful chemicals required
- Achieves sealing, airtightness, and watertightness requirements
Challenges:
- High requirements for part design necessitate specialized fixtures and welding heads
- Sensitive to material properties; certain plastics or metals are unsuitable for ultrasonic welding
- Relatively high initial equipment investment
7. FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: What materials can ultrasonic welding weld?
A: Primarily suitable for thermoplastics such as ABS, PP, and PC. It can also be used for thin-walled metals and aluminum foil, but specialized processes are required.
Q2: Will ultrasonic welding damage electronic components?
A: Under normal circumstances, it will not, because the vibration is confined to the welding surface. Precision electronic components are generally unaffected, but welding parameters must be controlled.
Q3: What is the difference between ultrasonic welding and hot plate welding?
A: Ultrasonic welding uses high-frequency vibration to quickly heat a localized welding surface, while hot plate welding heats the entire contact surface via a heating plate. Ultrasonic welding is faster, more precise, and requires no additional material.
Q4: How to choose the right ultrasonic welding equipment?
A: Select the frequency, power, welding head design, and automation level based on the part material, thickness, production volume, and precision requirements. Choose an experienced supplier for technical support.