By quanyu lee
2025-07-08 02:23:21
Welding Cable Guide
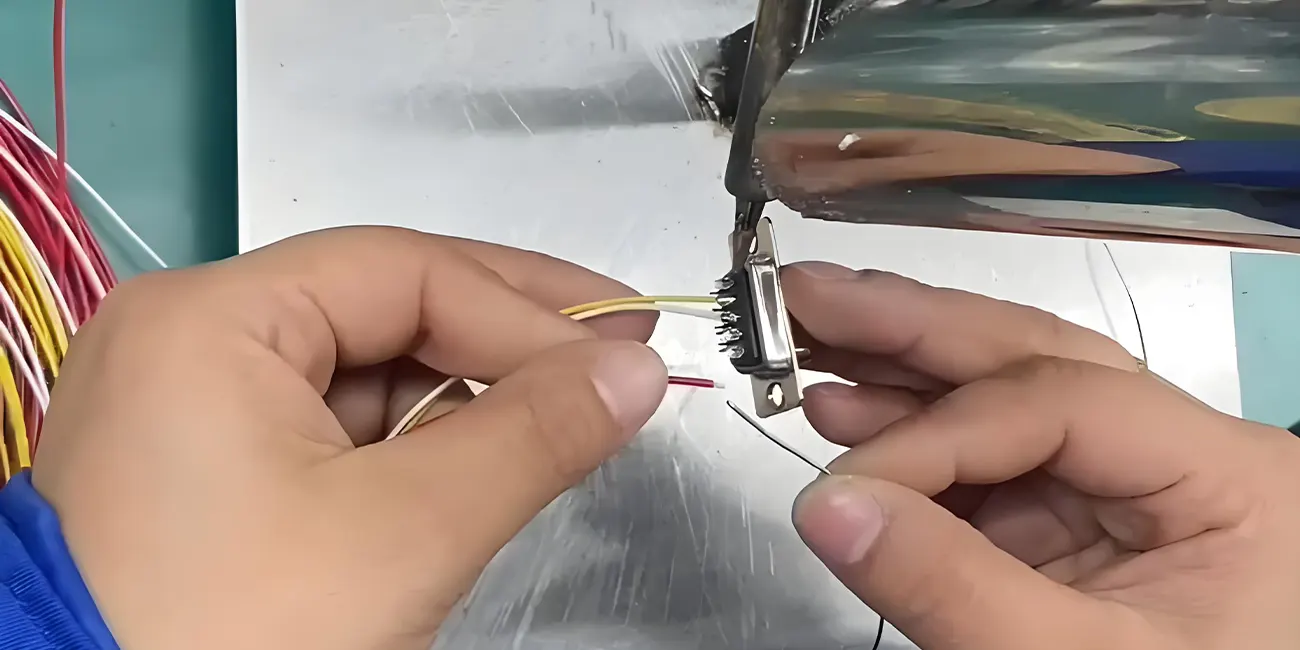
1. Basic definition of wire welding
Cable welding is a technical process that fuses the metal wires inside the wiring harness with the metal conductive contacts of the connector; Through the synergistic effect of heating and pressurization, a metallurgical bond is formed between the wiring harness and the connector, ensuring that the connector and the wiring harness have both reliable connection strength and stable and efficient data transmission conductivity; widely used in electronic equipment manufacturing, wire harness processing, and equipment assembly in the fields of electronics, electrical, automotive, aviation, etc.
2. Adverse conditions and explanations during welding
1. False welding
False soldering usually occurs when the solder joints appear to be connected on the surface, but in fact, they do not form a firm electrical connection. If you gently pull the solder joints, they will fall off. The main reason is that the tin melting time between the core wire and the connector is too short; the temperature during soldering is not high enough, and the solder is not fully melted. False soldering can cause electrical problems, such as short circuits and open circuits, in products, and in severe cases, even lead to equipment failure.
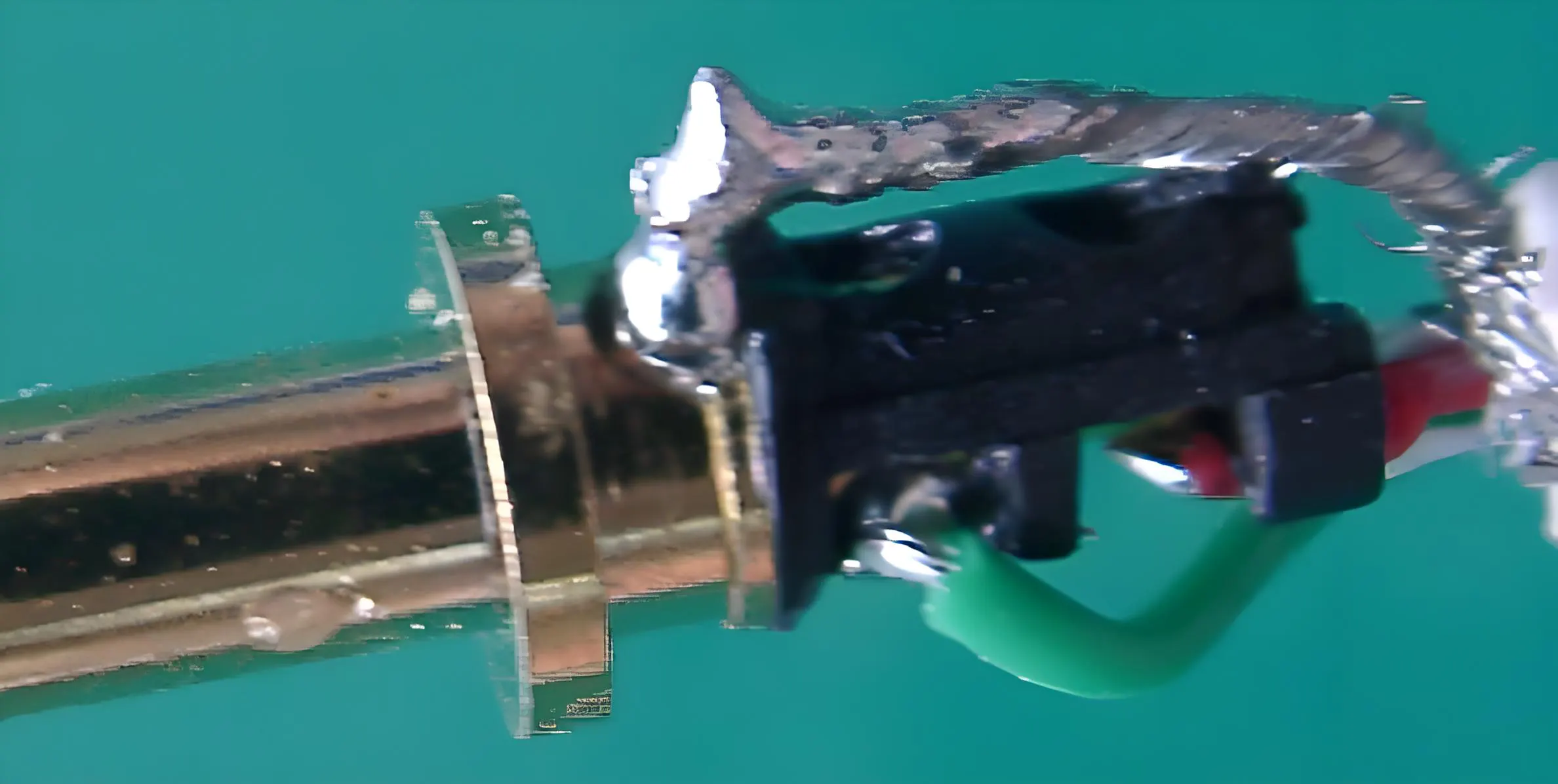

2. Cold welding
Cold welding occurs when the solder is attached to the surface of the metal being welded, but it has not completely melted or formed a strong alloy layer with the metal being welded. This is usually because the welding temperature is not high enough or the welding time is too short so that the solder cannot fully diffuse and fuse. The solder joint strength of cold welding is low, and it is easy to fall off, causing electrical problems in the product, such as circuit breakage.
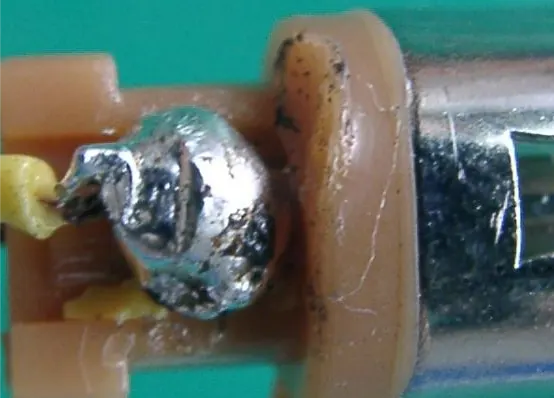
3. Too much solder
When too much solder is used during welding, the solder joints will be too large and unsightly, may easily form bridging solder joints, and may even cause short circuits between adjacent solder joints.
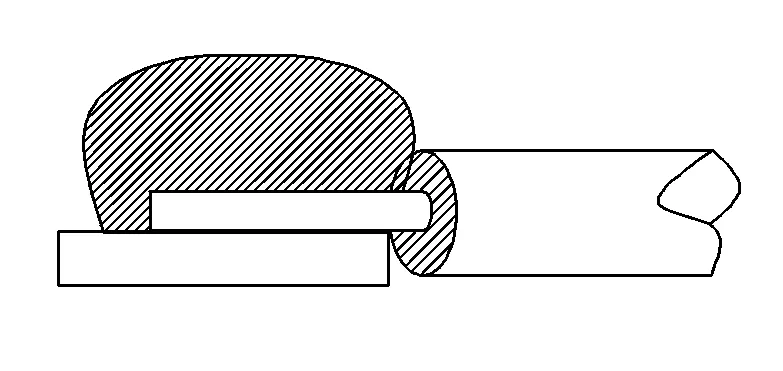
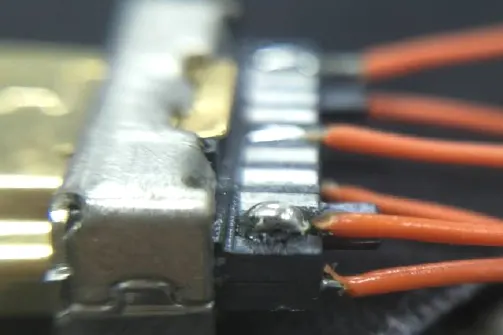
4. Too little solder
In contrast to too much solder, too little solder will prevent the tin point from completely wrapping the metal being soldered, resulting in insufficient connection strength, poor electrical contact, and poor adhesion.
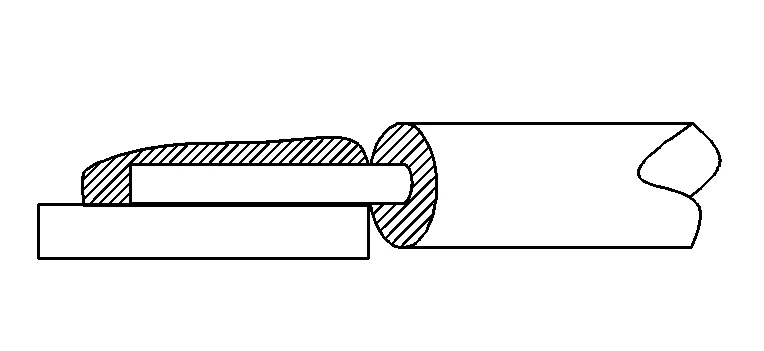

5. Solder point tip
Solder point tipping is manifested as sharp protrusions on the solder joints, which are usually caused by improper soldering iron withdrawal angle, slow withdrawal speed, etc. The solder point tipping leads to loose soldering.
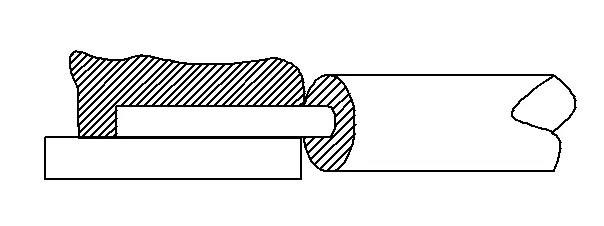
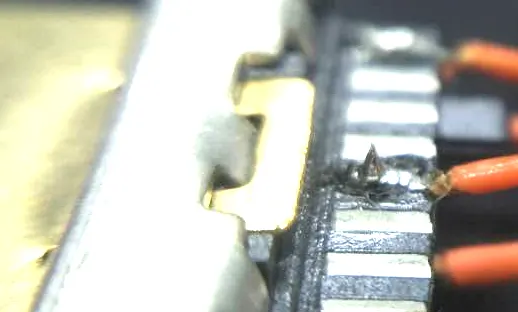
6. Conductor exposed
Exposed conductors usually mean that during welding, the conductor does not stick to the pad, and the tin point does not completely cover the conductor. It is easy for the conductivity to decrease due to oxidation and moisture, or it may break due to external friction. Long-term use may cause problems such as poor contact and leakage.
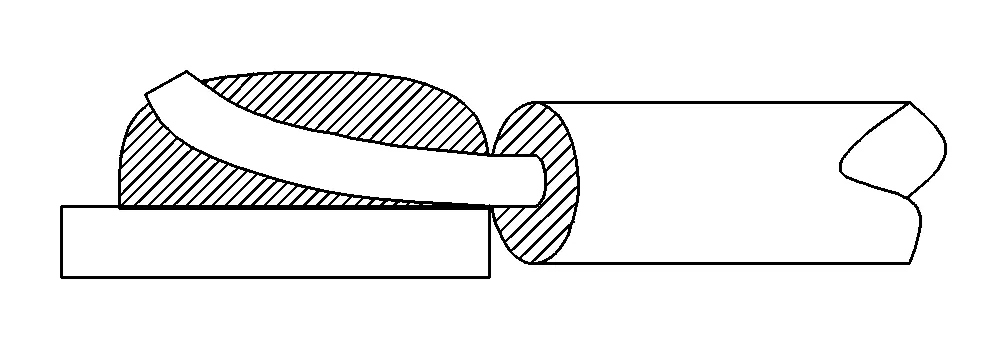

7. Conductor retraction
Conductor shrinkage is generally manifested as the conductor being attached to the pad during welding. If the conductor is exposed more than 0.5mm after shrinkage, it will reduce the welding area, easily cause breakage, and affect the stability of current transmission.
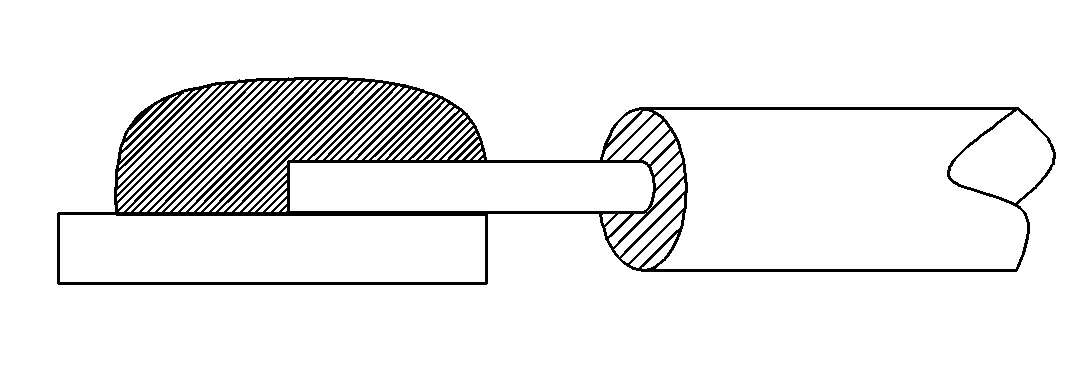
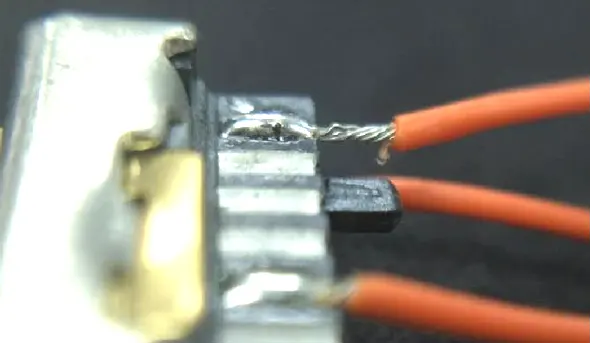
For Kaweei wire harness customization factory, to control the quality of wire welding, it is necessary to first understand the types, definitions, and common problems of welding. In actual production, the factory will strictly follow the welding process requirements and standardize each step of the operation process to reduce poor welding conditions and ensure that the customized wire harness welding is both reliable and stable.



